BITUMEN
- Home
- Products
- Bitumen
OXIDIZED BITUMEN
Leading companies usually have several advantages, such as pricing power, brand recognition and a loyal customer base. It takes time to achieve a dominant position in an industry, and maintaining that leadership position is an ongoing effort. Small businesses should first aspire to lead their respective local markets before planning for worldwide industry domination.
PENETRATION GRADE
In the past the penetration index was defined based on the assumption that thermal sensitivity in the bitumen used in road construction was zero. Bitumen is a thermoplastic material meaning that it becomes pliable or moldable above a specific temperature and returns to a solid state upon cooling.
Penetration grade bitumen is mainly used in road surfacing. Bitumen with lower penetration is used in regions with warm climates, while higher penetration grade is used in colder weather.
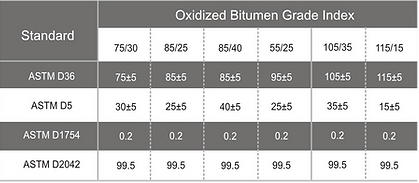
Penetration rate bitumen is graded based on penetration and softening point tests. This table describes the physicals propers of penetration grade bitumen is mainly used in road construction. During the last two decades of the 20th century, most road construction projects
showed inclination for solid bitumen which results in more effective asphalt.
VISCOSITY GRADE
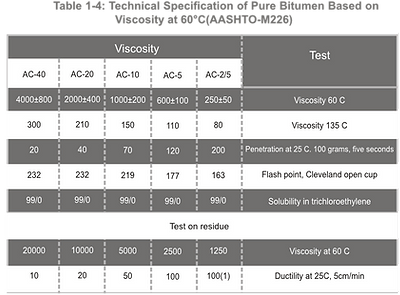
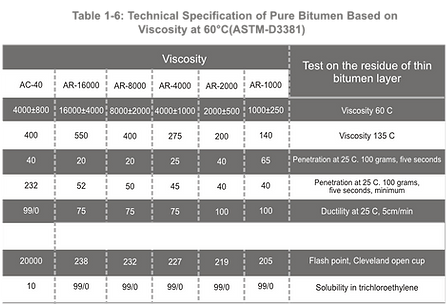
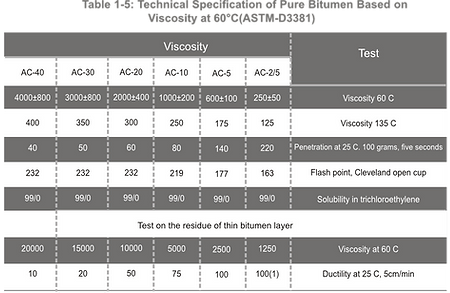
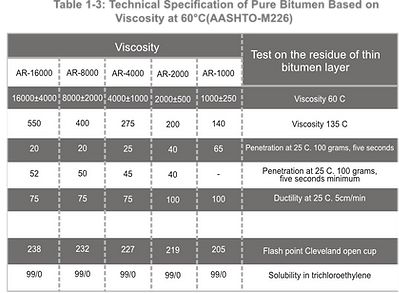
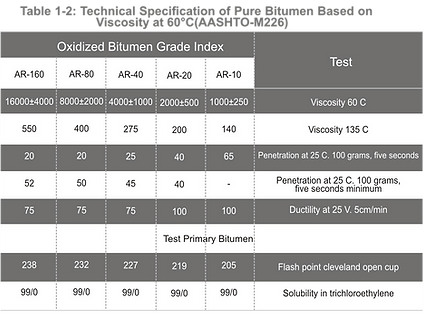
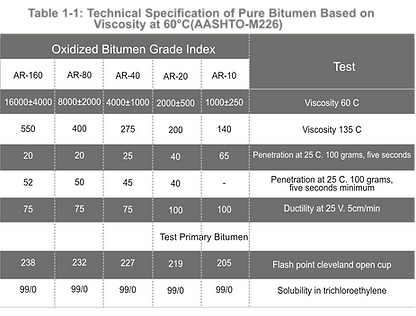
Bitumen is graded based on absolute viscosity at 60°C or kinematic viscosity at 135°C. The SI physical unit of dynamic viscosity is Poise, and kinematic viscosity is expressed in centi stokes. Pure bitumen has been graded based on AASHTO-M226and ASTM-d3381Standards. Tables 1-1to 1-6indicate tests and criteria.
CUTBACK BITUMEN
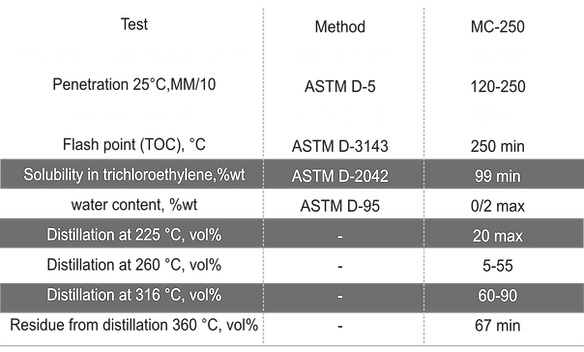
Bitumen is “cutback” by adding controlled amounts of petroleum distillates, such as kerosene. Type and quality of cutback depends on type an amount of solvent in the pure bitumen. The more solvent in cutback bitumen, leads to more viscosity in bitumen. Cutback bitumen is used when there is limited access to heating equipment, bitumen decomposition in high temperature, bitumen cooling throughout working, consuming. This type of bitumen is used in road operations forworkers safety, fire and time surfacing and pavement. Medium-Curing (MC) bitumen is achieved from solving pure bitumen into kerosene. Cutback bitumen is classified based on viscosity arad. It is divided into three categories:
Slow-curing may be achieved from solving bitumen in gas oil or fuel oil or directly from the distillation of crude oil. SC cutbacks do not evaporate on the normal weather conditions, but they gradually experience changes in their molecular form. This kind of bitumen is achieved by solving bitumen 85/100 in a heavy solvent such as gas oil or fuel oil which will not only evaporate but also make it hard. Types of this kind of bitumen include SC 70,SC,250,SC 800 and SC 3000.
MC cutback are prepared by solving bitumen in kerosene which evaporates more slowly than gasoline. MC cutbacks are divided into five groups with their viscosity varying from 3-4 to 6,000 at 60 degrees centigrade. This kind of bitumen maybe achieved by solving bitumen 85/100 in kerosene.
The cutback bitumen is known as rapid-suring(RC) if the bitumen is solved in gasoline. The reason is that evaporation occurs quickly and the bitumen is deposited. RC cutbacks are divided into RC70,RC800 and RC 3000 categories. The numbers indicate the viscosity of bitumen. Naphtha could be mixes w i t h bitumen 80/100 for more dilution.



